Servo Motor Advantage
Servos are known to always be frequent and work at the same pace. So, if a heavy load is placed on the motor, the driver will increase the current to the motor coil as it rotates the motor. This basically means that servo motors are expected to always be mechanically on point. And because of its precision, it allows companies to operate it at a high-speed pace.
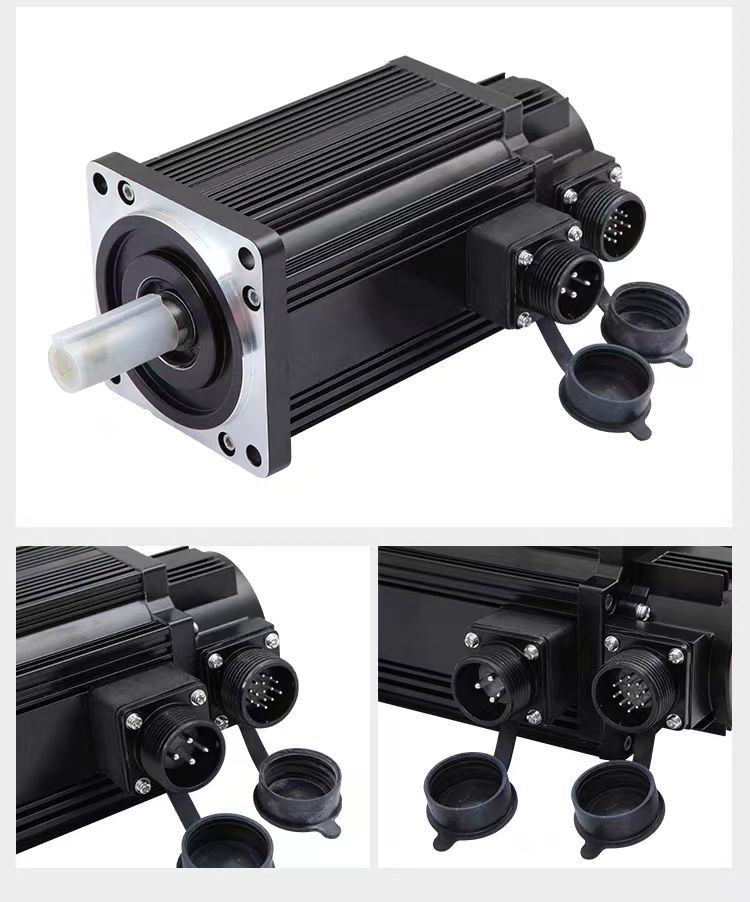

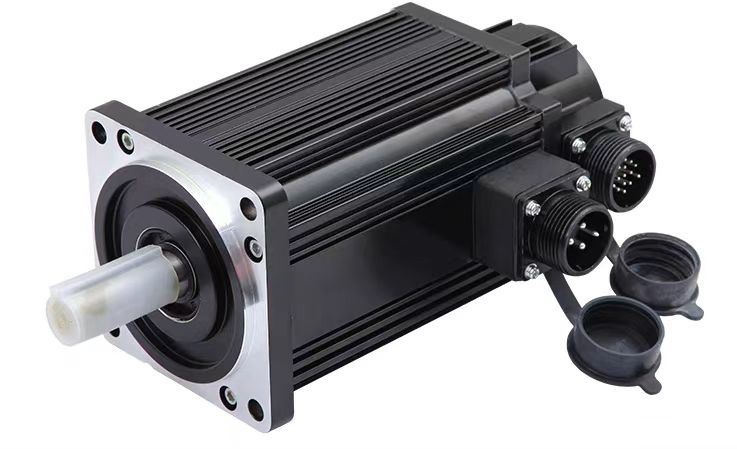
Product Name: Servo Motor
Rated Voltage: 220v /380v
Rated Speed: 3000rpm /1500rpm /or customized
Rated Torque: Customized
Rated Current: Customized
Rated Power: 400w~5.5kw
Dozens of parts make up a servo motor with each and every single part playing a vital role in the device’s functionality. Here are its most important parts and the significant roles they play in the functionality of the servos.
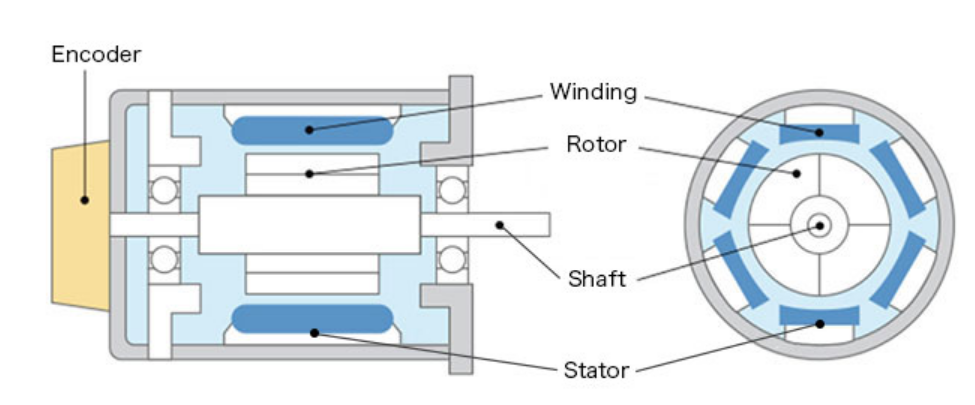
Stator - A stator creates a rotating magnetic field to efficiently generate torque.
Winding - Current flows in the winding produces a rotating magnetic field.
Shaft - The shaft transmits the motor output power. This load is driven through the transfer mechanism.
Rotor - A rotor is a permanent magnet that is positioned externally to the shaft.
Encoder - An optical encoder always observes and calculates the number of rotations being completed and watches the position of the shaft.
Each part of the servo motor serves a huge purpose in making the servos properly function or work.